The Procedure

Beach chair position surgery is a surgical technique where the patient is positioned in a semi-sitting posture, resembling a beach chair, to facilitate surgical access to specific anatomical areas. This position is commonly used for procedures involving the head, neck, shoulders, and upper extremities.
Steps Involved in Beach Chair Position Surgery
The procedure involves a series of steps to ensure patient safety and surgical success.
- Patient Preparation: The patient undergoes a thorough medical evaluation, including a review of their medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. This helps identify any potential risks or complications and ensure the patient is suitable for the procedure. Anesthesia is administered, either general or regional, depending on the specific surgery and patient preference.
- Positioning: The patient is carefully positioned on the operating table in a semi-sitting posture, resembling a beach chair. The patient’s head is supported by a headrest, and their arms are positioned on armrests. This position allows for optimal surgical access to the target area, minimizing strain on the patient’s neck and spine.
- Surgical Incision: A surgical incision is made in the target area, allowing the surgeon to access the underlying tissues and structures. The incision is made using a scalpel, and the surgeon carefully dissects the tissues to expose the surgical field.
- Surgical Procedure: The surgeon performs the specific surgical procedure, using a variety of instruments and techniques. This may involve removing tissue, repairing damaged structures, or implanting devices.
- Closure: Once the surgical procedure is complete, the surgeon closes the surgical incision using sutures, staples, or other closure techniques. This helps to minimize bleeding, promote healing, and prevent infection.
- Postoperative Care: After surgery, the patient is monitored closely for any complications and receives appropriate postoperative care. This may include pain management, wound care, and physical therapy.
Instruments Used
The specific instruments used in beach chair position surgery vary depending on the type of procedure being performed. However, some common instruments include:
- Scalpels: Used to make surgical incisions.
- Forceps: Used to grasp and manipulate tissues.
- Scissors: Used to cut tissues and sutures.
- Retractors: Used to hold tissues out of the way of the surgical field.
- Suction: Used to remove blood and fluids from the surgical field.
- Electrocautery: Used to seal blood vessels and prevent bleeding.
- Sutures: Used to close surgical incisions.
- Staples: Used to close surgical incisions.
Anesthesia, Beach chair position surgery
Anesthesia is administered to the patient to ensure their comfort and prevent pain during surgery. The type of anesthesia used depends on the specific procedure and patient preference.
- General Anesthesia: This involves putting the patient to sleep, rendering them unconscious and pain-free. General anesthesia is typically used for longer and more complex procedures.
- Regional Anesthesia: This involves numbing a specific area of the body, such as the neck or shoulder. Regional anesthesia is often used for shorter and less invasive procedures.
Rationale for Using the Beach Chair Position
The beach chair position offers several advantages for specific surgical procedures.
- Improved Surgical Access: The semi-sitting posture provides excellent surgical access to the head, neck, shoulders, and upper extremities. This allows the surgeon to operate with greater precision and control, minimizing the risk of complications.
- Reduced Strain on the Neck and Spine: The beach chair position helps reduce strain on the patient’s neck and spine, as compared to other surgical positions. This is particularly important for patients undergoing procedures on the head, neck, or shoulders.
- Improved Airway Management: The semi-sitting posture helps maintain a clear airway, which is essential for patients undergoing general anesthesia. This position allows for easier intubation and ventilation, reducing the risk of airway complications.
However, the beach chair position also has some disadvantages.
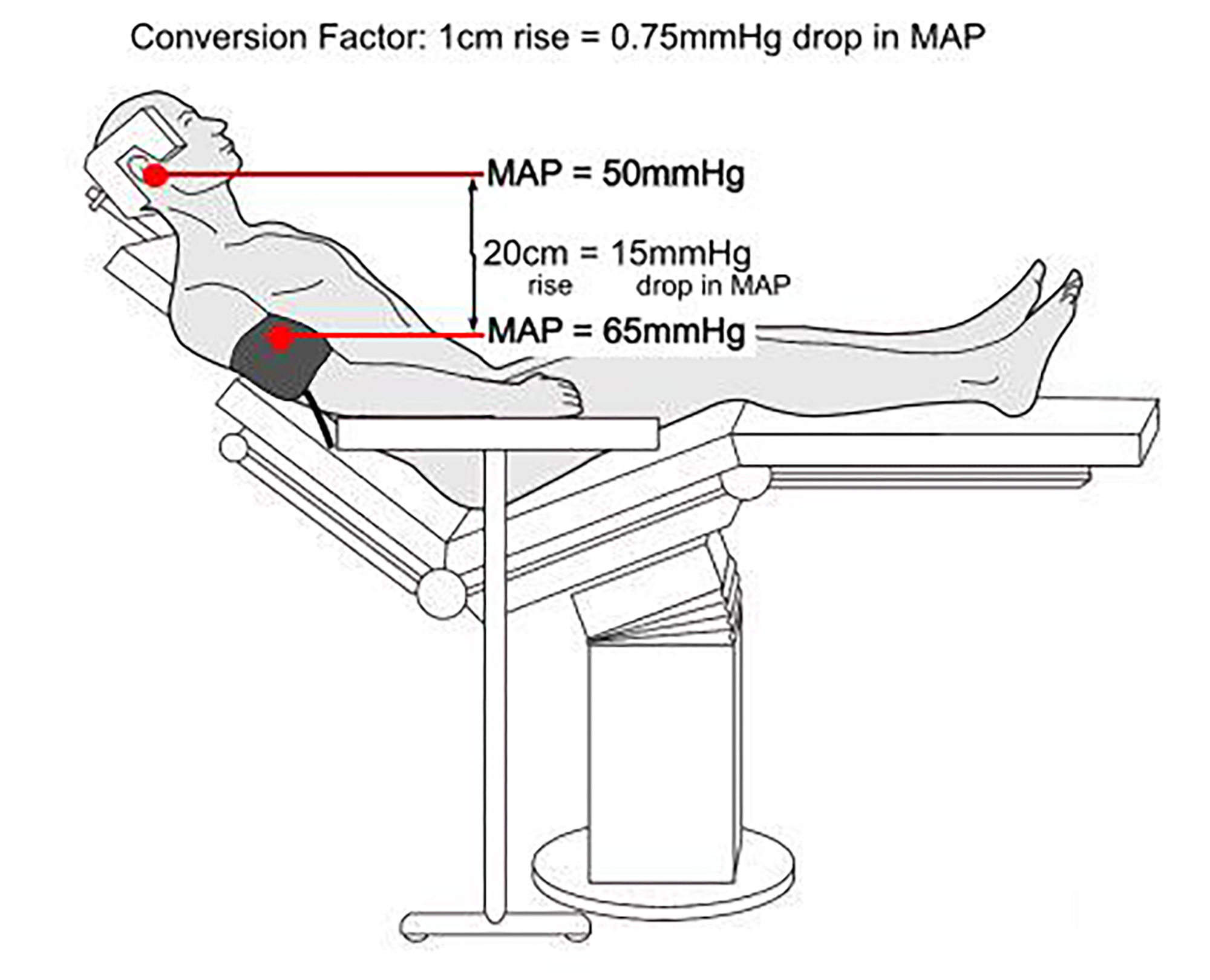
- Increased Risk of Blood Pressure Fluctuations: The semi-sitting posture can cause changes in blood pressure, which may increase the risk of complications. This is particularly important for patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
- Limited Mobility: The beach chair position limits the patient’s mobility, which can make it difficult to perform certain procedures. This is especially true for procedures involving the lower extremities or abdomen.
Comparison with Other Surgical Positions
The beach chair position is commonly used for surgeries involving the head, neck, shoulders, and upper extremities. Other surgical positions, such as the supine (lying on the back) and prone (lying on the stomach) positions, are used for procedures involving other anatomical areas.
- Supine Position: The supine position is a common surgical position used for procedures involving the abdomen, chest, and extremities. It is a relatively comfortable position and allows for easy access to these areas. However, the supine position can make it difficult to access the head, neck, and shoulders.
- Prone Position: The prone position is used for procedures involving the spine, back, and buttocks. It allows for optimal access to these areas but can be uncomfortable for the patient and may increase the risk of airway complications.
Benefits and Risks: Beach Chair Position Surgery
The beach chair position, also known as the semi-Fowler’s position, has gained popularity in various surgical procedures due to its potential advantages for both the patient and the surgeon. This position involves elevating the patient’s upper body to an angle of 30-45 degrees, with their legs slightly elevated. This article will explore the potential benefits and risks associated with this surgical positioning.
Benefits
The beach chair position offers several potential benefits, particularly for procedures involving the head, neck, and upper extremities.
- Improved airway management: Elevating the patient’s head and shoulders facilitates airway management, reducing the risk of airway obstruction and allowing for easier intubation and ventilation. This is particularly crucial for patients with pre-existing respiratory conditions or those undergoing procedures that involve the head and neck.
- Enhanced surgical exposure: The beach chair position provides better access to the surgical field, especially for procedures involving the head, neck, and shoulders. The elevated position allows surgeons to work more comfortably and with improved visualization, potentially leading to more precise surgical maneuvers.
- Reduced risk of venous air embolism: This position helps minimize the risk of venous air embolism, a serious complication that can occur when air enters the bloodstream. The elevation of the upper body reduces the likelihood of air entering the veins in the neck and chest.
- Increased patient comfort: The beach chair position can improve patient comfort by reducing pressure on the back and abdomen, allowing for better ventilation and reducing the risk of nausea and vomiting. This can be particularly beneficial for patients undergoing long procedures.
- Faster recovery: The beach chair position may promote faster recovery by reducing postoperative pain and discomfort, allowing for earlier mobilization and discharge from the hospital. This is particularly important for patients undergoing minimally invasive procedures or those with underlying medical conditions.
Risks
While the beach chair position offers several benefits, it also carries certain risks that surgeons must carefully consider before deciding to use it.
- Hypotension: Elevating the upper body can lead to a decrease in blood pressure, particularly in patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions. This can be exacerbated by blood loss during surgery, requiring close monitoring and appropriate management.
- Nerve injury: Prolonged pressure on nerves in the upper extremities or neck can lead to nerve injury, causing numbness, tingling, or weakness. This risk can be mitigated by proper padding and positioning of the patient’s limbs and head.
- Airway obstruction: While the beach chair position can improve airway management, it can also lead to airway obstruction if not carefully managed. This risk is particularly high in patients with pre-existing respiratory conditions or those undergoing procedures that involve the head and neck.
- Cardiovascular complications: The beach chair position can also increase the risk of cardiovascular complications, such as arrhythmias or myocardial ischemia, especially in patients with pre-existing heart conditions. This requires careful monitoring and appropriate management.
- Increased risk of falls: The beach chair position can make it more difficult for patients to move or get out of bed, increasing the risk of falls. This risk can be mitigated by providing appropriate assistance and ensuring a safe environment for the patient.
Examples
The beach chair position has been used successfully in various surgical procedures, including:
- Spine surgery: This position allows for optimal exposure of the cervical and thoracic spine, making it suitable for procedures such as spinal fusion and decompression surgery.
- Head and neck surgery: The beach chair position is often used for procedures involving the head and neck, such as thyroid surgery, parathyroid surgery, and carotid endarterectomy. This position provides excellent access to the surgical field and allows for improved visualization.
- Breast surgery: The beach chair position can be beneficial for certain breast surgeries, such as lumpectomy and breast reconstruction, providing better access to the surgical field and reducing the risk of complications.
Case Examples
- Beneficial Case: A 65-year-old patient with cervical spondylosis underwent a cervical fusion surgery in the beach chair position. The position allowed for excellent exposure of the cervical spine, enabling the surgeon to perform the procedure with precision and minimize complications. The patient recovered well with minimal postoperative pain and was able to return to normal activities within a few weeks.
- Problematic Case: A 72-year-old patient with a history of hypertension and heart disease underwent a carotid endarterectomy in the beach chair position. During the procedure, the patient experienced a significant drop in blood pressure, requiring immediate intervention. The patient recovered but the case highlights the importance of careful patient selection and monitoring during procedures in the beach chair position.
Beach chair position surgery might sound strange, but it’s a real procedure used for certain spinal conditions. After surgery, you’ll want to relax and recover in a comfortable spot, and what better than a pallet wood patio chair on your porch?
They’re sturdy, eco-friendly, and perfect for enjoying the sunshine while you heal. And once you’re back on your feet, you can enjoy those chairs for years to come!
Beach chair position surgery is a unique approach that allows surgeons to operate with better visibility and access to certain areas of the body. This technique is often used for procedures involving the spine or pelvis, and it’s interesting to consider how this medical innovation relates to the cultural significance of a janie show wood chair , a symbol of comfort and relaxation.
Both the beach chair position in surgery and the janie show wood chair represent a focus on achieving optimal comfort and positioning for a specific purpose, whether it’s for healing or simply enjoying a moment of leisure.
